Blog article
- 5 minutes read
- Sendmarc
The cost of impersonation: a threat that could lose your organization millions
With digital technology advancing at a rapid rate, impersonation attacks are becoming increasingly prevalent, resulting in financial loss for organizations all over the world.

When it comes to the motivation behind impersonation attacks, the 2022 Verizon Data Breach Incidents Report advises that 85% of them are financially motivated.
Types of impersonation attacks
Impersonation attacks can take a variety of different forms; most notably through phishing, spoofing, and social engineering scam emails.
Phishing attacks include the sending of fraudulent emails to steal passwords, account numbers, and other sensitive information. Phishing scams – which account for 70% of all advanced attacks, making them the most common type of attack – are a numbers game with attackers sending thousands of fraudulent emails in the hope that just a small percentage of recipients fall for it. There are common techniques employed by attackers with regards to how phishing emails are crafted that aim to increase their chances of success.
Spoofing attacks are a class of phishing attack that go one step further with fraudulent emails masterfully disguised to appear as if they come from a legitimate, trustworthy source. Broadly defined, a spoofing scam is whenever an online scammer disguises their identity to be perceived as a representative from a legitimate organization. Incidentally, Apple, DropBox and PayPal are among the few king targets for cybercrime, including spoofing attacks – Apple accounting for 27.2% of all phishing scams.
Social engineering attacks refer to a variety of techniques employed by cybercriminals to fool targets into divulging sensitive information, or taking certain actions that compromise security. According to Gitnux 2023’s Overview Statistic report, a paper submitted to the U.S. Internet Crime Complaint Center, conveyed a staggering 324 thousand individuals affected by cybercrime alone in 2021. The report further confirms that 90% of data breaches in a company have social engineering components; thus further highlighting the need for organizations to tighten their cyber security measures.
Real-world cost of impersonation attacks
When it comes to the cost of impersonation attacks, in terms of financial loss, and reputational damage, it can be staggering.
The Cost of a Data Breach Report 2022 by IBM reported that the average cost of a data breach from a social engineering attack is around$4.35 million, climbing a noteworthy 12.7% from the results featured in the 2020 Report. At the top of the list, the average cost of a data breach with a phishing scam as the initial attack vector was reported as $4.91 million. The below graph is from the report and shows the top initial attack vectors by percentage of breaches and average cost:
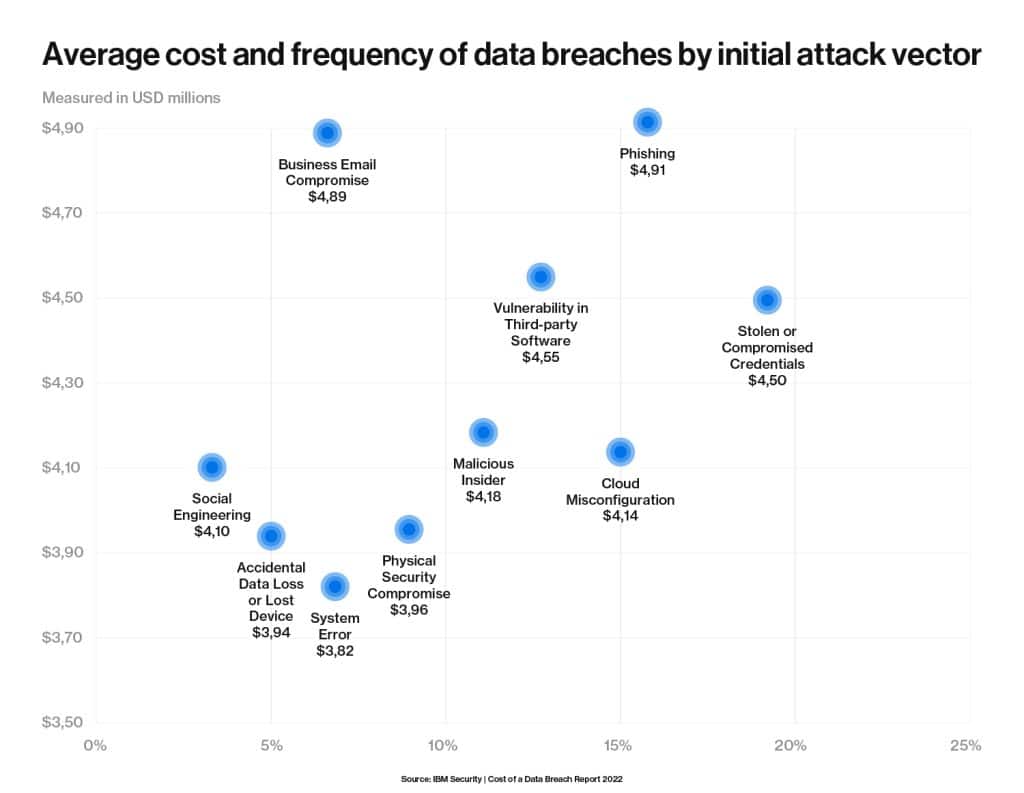
A real-world case study demonstrating the cost of an impersonation attack is Nikkei Inc, which lost a substantial sum of $29 million. A fraudulent email was sent to a subsidiary of Nikkei in the United States, impersonating a legitimate vendor, instructing the targeted recipient to transfer funds into a fraudulent account. This attack resulted in the loss of millions of dollars, showing that sometimes the most effective impersonation attacks can also be the most simple.
Another real-world example is the impersonation attack that targeted the Canadian city of Saskatoon. A fraudulent email was sent to the city, impersonating a construction company with whom the city was doing business. The email instructed them to update the payment details for an upcoming payment and resulted in $1 million being transferred into a fraudulent account.
The Toyota Boshoku Corporation also fell victim to an impersonation attack that saw them lose $37 million, as a result of a fraudulent email sent to a subsidiary in Thailand, impersonating a senior executive at the company. The email instructed the subsidiary to transfer funds into a fraudulent account.
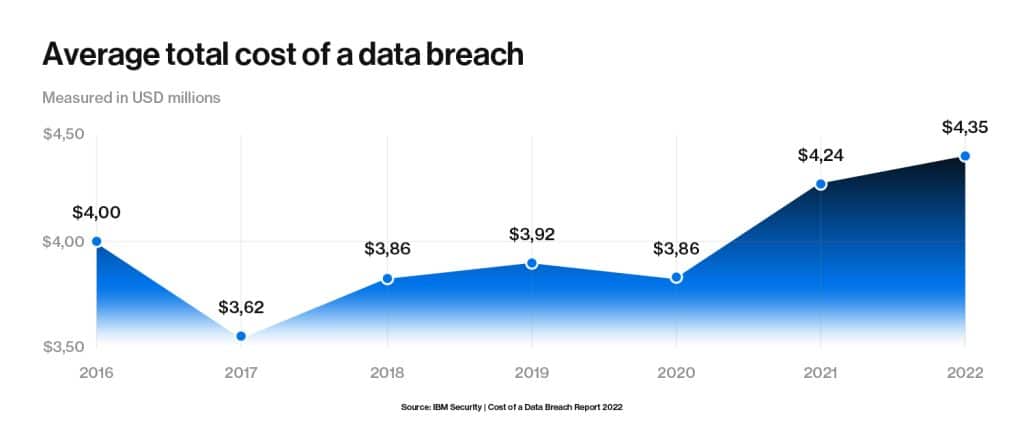
The Cost of Data Breach Report found that in comparison to prior years, 2022 achieved a record high in the average cost of a data breach.
Damage to reputation
While the financial loss of impersonation attacks are enough cause for concern, an added risk is the damage that’s done to an organization’s reputation.
In 2021, Ubiquiti Networks Inc was hit by an email phishing attack that resulted in a data breach. The attackers gained access to customers’ email addresses, shipping addresses, and phone numbers, causing reputational damage to the company due to diminished trust in its ability to protect customers’ information. A year later, Ubiquiti also lost $46.7 million as a result of a spoofing attack, demonstrating how convincing cyberattacks can be – even when an organization has been targeted previously!
The Democratic National Committee (DNC) was the target of a phishing email attack by Russian hackers, who gained access to the organization’s email accounts and leaked thousands of sensitive emails during the U.S. presidential election. The emails contained controversial content, which inspired accusations of bias, causing significant reputational damage to the DNC.
Not only do these case studies highlight the ease with which impersonation attacks can succeed, they also demonstrate how quickly a reputation can be damaged when an organization is perceived to be unable to protect sensitive information – its own, and that of its customers.
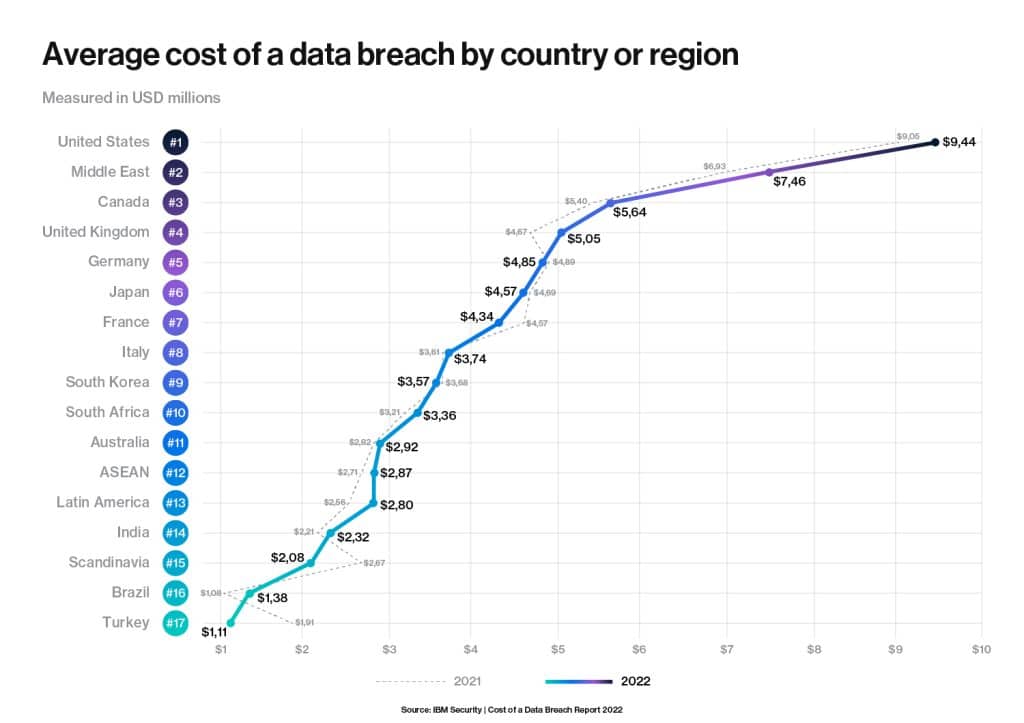
The Cost of Data Breach Report found that the United States recorded the highest average cost of a data breach for the 12th year in a row.
The graph below shows a comparison of the average data breach costs by country or region in 2021 and 2022.
Prevention and mitigation
Preventing, and mitigating the damage of impersonation attacks requires a multi-faceted approach, involving both technical and non-technical interventions.
One key technical intervention is the implementation of DMARC, an email authentication protocol that enables organizations to protect their domains from spoofing and phishing attacks. DMARC guarantees exceptional security that reduces the risk of impersonation attacks, by enabling organizations to protect themselves from impersonation and phishing attacks.
As demonstrated by the prevalence and regularity of impersonation attacks, it’s clear that every organization is at risk from email fraudsters.